
|
|
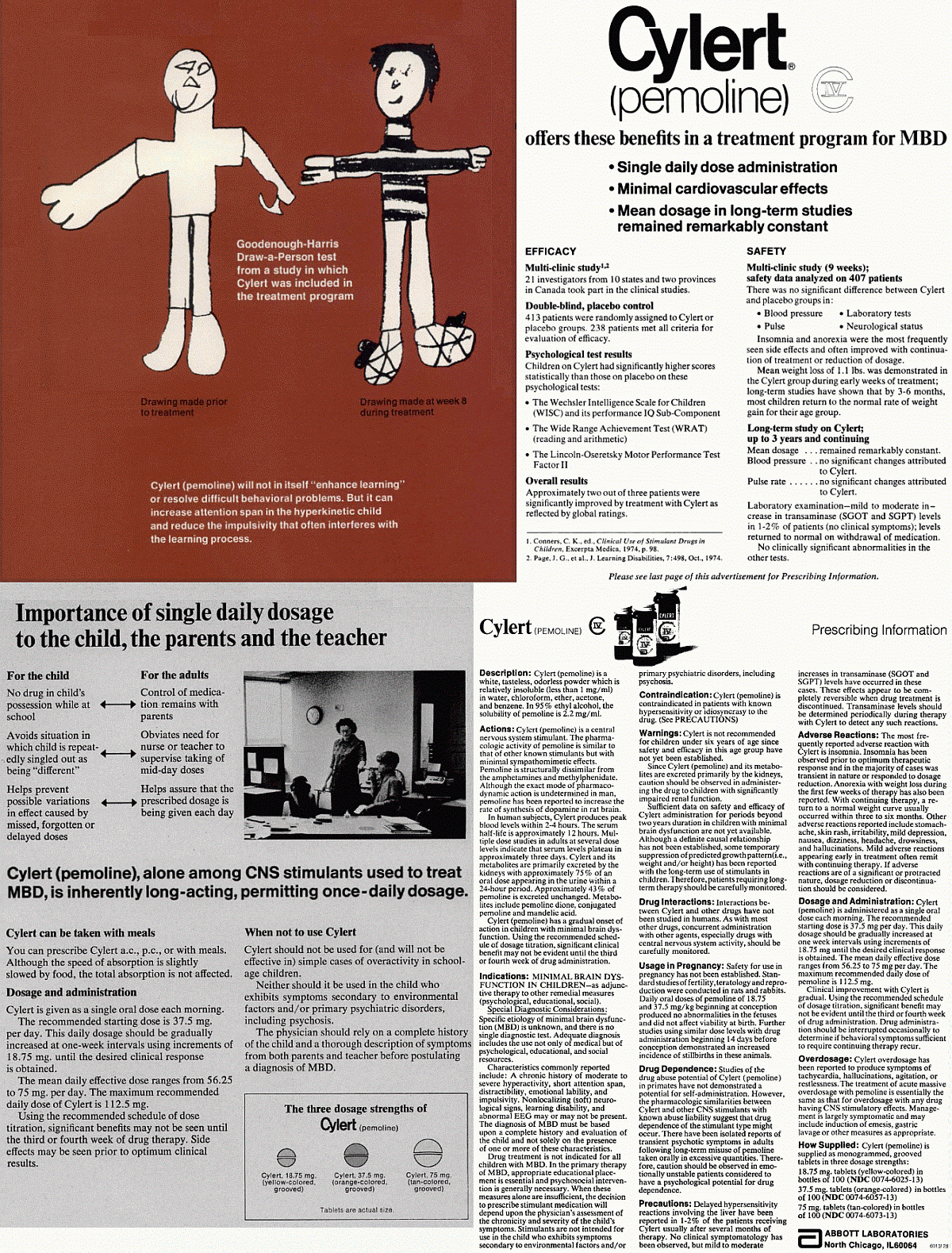
Cylert advertisement, 1976. American Journal of Diseases of Children, Vol. 130, No. 1, pp. 84-87. Goodenough-Harris Draw-a-Person test from a study in which Cylert was included in the treatment program Drawing made prior to treatment ~ Drawing made at week 8 during treatment Cylert (pemoline) will not in itself "enhance learning" or resolve difficult behavioral problems. But it can increase attention span in the hyperkinectic child and reduce the impulsivity that often interferes with the learning process. Psychological test results Children on Cylert had significantly higher scores statistically than those on placebo on these psychological tests: * The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) and its performance IQ Sub-Component * The Wide Range Achievement Test (WRAT) (reading and arithmetic) * The Lincoln-Oseretsky Motor Performance Test Factor II Side effects may be seen prior to optimum clinical results. When not to use Cylert Cylert should not be used for (and will not be effective) in simple cases of overactivity in school-age children. Neither should it be used in the child who exhibits symptoms secondary to environmental factors and/or primary psychiatric disorders, including psychosis. The physician should rely on a complete history of the child and a thorough description of symptoms from both parents and teacher before postulating a diagnosis of MBD. Indications: MINIMAL BRAIN DYSFUNCTION IN CHILDREN - as adjunctive therapy to other remedial measures (psychological, educational, social). Special Diagnostic Considerations: Specific etiology of minimal brain dysfunction (MBD) is unknown, and there is no single diagnostic test. Adequate diagnosis includes the use not only of medical but of psychological, educational, and social resources. Characteristics commonly reported include: A chronic history of moderate to severe hyperactivity, short attention span, distractibility, emotional lability, and impulsivity. Nonlocalizing (soft) neurological signs, learning disability, and abnormal EEG may or may not be present. The diagnosis of MBD must be based on a complete history and evaluation of the child and not solely on the presence of one or more of these characteristics. Drug treatment is not indicated for all children with MBD. In the primary therapy of MBD, appropriate educational placement is essential and psychosocial intervention is generally necessary. When these measures alone are insufficient, the decision to prescribe stimulant medication will depend upon the physician's assessment of the chronicity and severity of the child's symptoms. Stimulants are not intended for use in the child who exhibits symptoms secondary to environmental factors and/or primary psychiatric disorders, including psychosis. Abbott Laboratories North Chicago, IL 60064 In May 2005, Abbott voluntarily chose to stop sales and marketing of Cylert in the U.S. In October 2005, the FDA ruled "the overall risk of liver toxicity from Cylert and generic pemoline products outweighs the benefits of this drug," after allowing it on the U.S. market for 30 years. |