
|
|
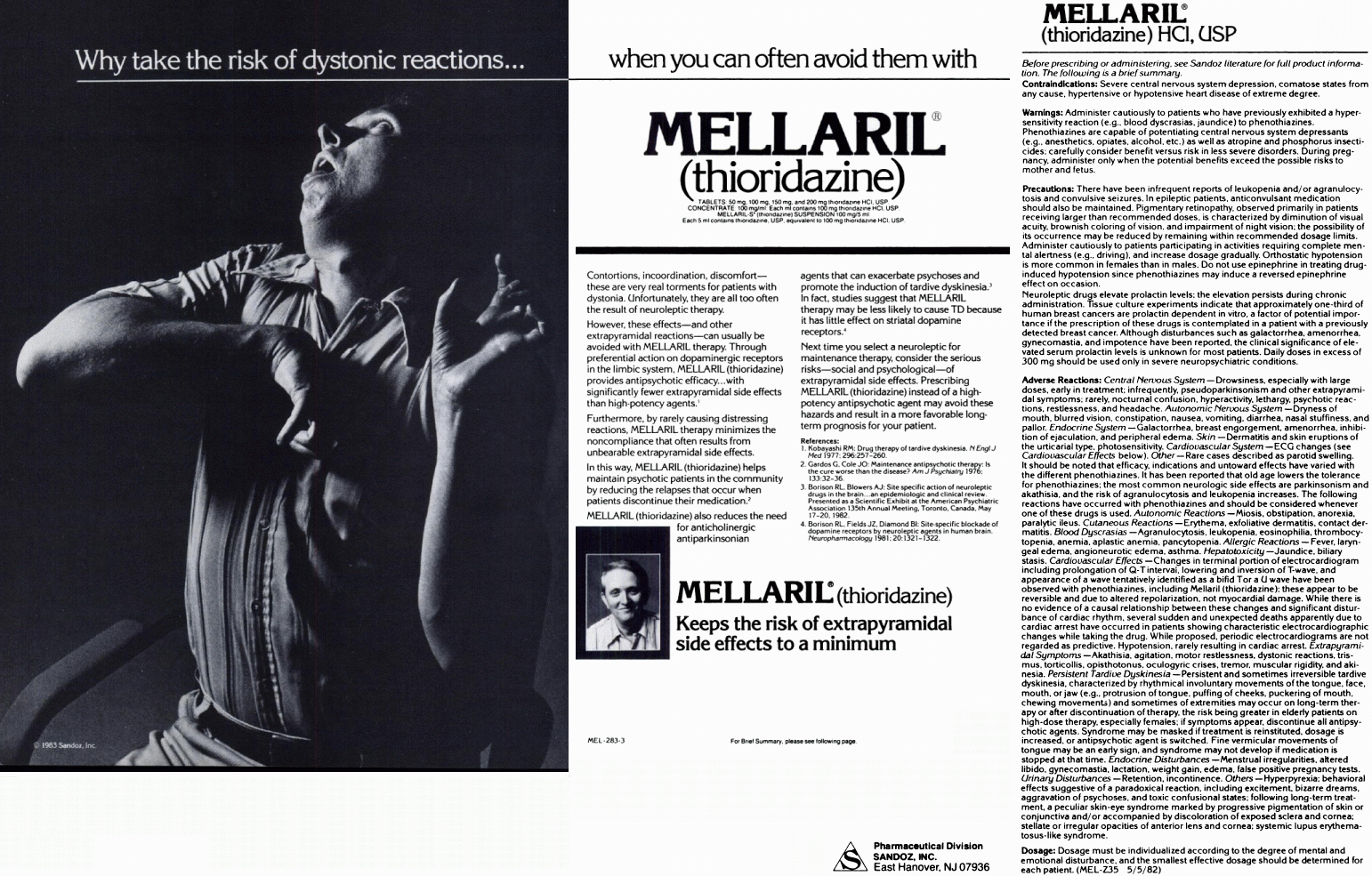
Mellaril advertisement, 1983. Hospital & Community Psychiatry, Vol. 34, No. 8. Why take the risk of dystonic reactions... when you can often avoid them with Mellaril® (thioridazine) Contortions, incoordination, discomfort -- these are very real torments for patients with dystonia. Unfortunately, they are all too often the result of neuroleptic therapy. However, these effects -- and other extrapyramidal reactions -- can usually be avoided with Mellaril therapy. Through preferential action on dopaminergic receptors in the limbic system, Mellaril (thioridazine) provides antipsychotic efficacy... with significantly fewer extrapyramidal side ffects than high-potency agents.(1) Furthermore, by rarely causing distressing reactions, Mellaril therapy minimizes the noncompliance that often results from unbearable extrapyramidal side effects. In this way, Mellaril (thioridazine) helps maintain psychotic patients in the community by reducing the relapses that occur when patients discontinue their medication.(2) Mellaril (thioridazine) also reduces the need for anticholinergic antiparkinsonian agents that can exacerbate psychoses and promote the induction of tardive dyskinesia.(3) In fact, studies suggest that Mellaril therapy may be less likely to cause TD because it has little effect on striatal dopamine receptors.(4) Next time you select a neuroleptic for maintenance therapy, consider the serious risks -- social and psychological -- of extrapyramidal side effects. Prescribing Mellaril (thioridazine) instead of a high-potency antipsychotic agent may avoid these hazards and result in a more favorable long-term prognosis for your patient. References: 1. Kobayashi RM: Drug therapy of tardive dyskinesia. N Engl J Med 1977: 296:257-260. 2. Gardos G, Cole JO: Maintenance antipsychotic therapy: Is the cure worse than the disease? Am J Psychiatry 1976: 133:32-36. 3. Borison RL, Blowers AJ: Site specific action of neuroleptic drugs in the brain... and epidemiologic and clinical review. Presented as a Scientific Exhibit at the American Psychiatric Association 135th Annual Meeting, Toronto, Canada, May 17-20, 1982. 4. Borison RL, Fields JZ, Diamond BI: Site-specific blockade of dopamine receptors by neuroleptic agents in human brain. Neuropharmacology 1981: 20:1321-1322. MELLARIL® (thioridazine) keeps the risk of extrapyramidal side effects to a minimum For Brief Summary, please see the following page. Pharmaceutical Division SANDOZ, INC. East Hanover, NJ 07936 |