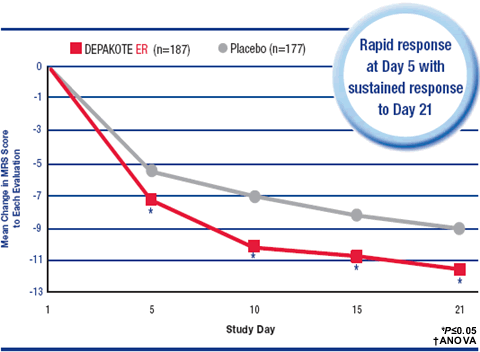
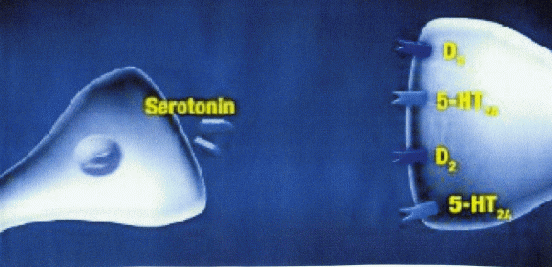
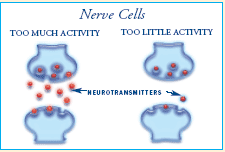
The symptoms of bipolar disorder are thought to be caused by an imbalance of key chemicals in the brain. The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells that move a constant stream of information from one to the other. To keep the information flowing, the cells release chemicals known as "neurotransmitters." Two key neurotransmitters that are needed for brain function are dopamine and serotonin, which play a crucial role in emotional health.
Many scientists believe that when the levels of these neurotransmitters aren't quite right, it may result in bipolar disorder. For instance, too much dopamine in certain parts of the brain can cause symptoms such as delusions, while too little dopamine in other parts of the brain can cause symptoms such as a lack of emotion and energy.
The exact way Abilify (or any other medicine for bipolar disorder) works is unknown. However, experts believe that Abilify works by adjusting dopamine and serotonin, two brain chemicals that play a crucial role in emotional health.


The most commonly observed adverse events associated with Abilify were: an inner sense of restlessness or need to move (akathisia), constipation, and accidental injury. Other common side effects are: headache, agitation, anxiety, insomnia, nausea, upset stomach, sleepiness, lightheadedness, vomiting, and tremor. Adverse events that occurred in 2% or more of patients treated with Abilify: blurred vision; nausea, vomiting, constipation, dyspepsia, dry mouth, abdominal discomfort, stomach discomfort, salivary hypersecretion; fatigue, pain, peripheral edema, arthralgia, pain in extremity; headache, dizziness, akathisia, sedation, extrapyramidal disorder, tremor, somnolence; anxiety, insomnia, restlessness; pharyngolaryngeal pain, cough, nasal congestion; hypertension.

© 2006 Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. All Rights Reserved.