
What you need to know about schizophrenia
Although the exact cause is not known, many scientists believe that schizophrenia is brought on by an imbalance of key chemicals in the brain, called neurotransmitters. Learn more about the way that Abilify is thought to adjust the balance of key chemicals in the brain.
View the video, The Brain, Schizophrenia, and Abilify.
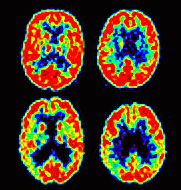
 The human brain is made up of billions of nerve cells. These cells communicate by releasing chemicals known as "neurotransmitters." Two key neurotransmitters that are needed for brain function are dopamine and serotonin, which play a crucial role in emotional health.
The human brain is made up of billions of nerve cells. These cells communicate by releasing chemicals known as "neurotransmitters." Two key neurotransmitters that are needed for brain function are dopamine and serotonin, which play a crucial role in emotional health.
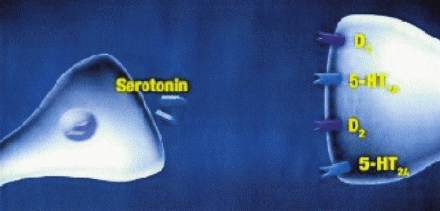
It is believed that schizophrenia is a result of an imbalance of dopamine and serotonin, with too much of these chemicals in certain areas of the brain and too little in others. Pharmacological treatments for schizophrenia aim to balance the levels of one or both of these neurotransmitters.
How Abilify is Thought to Work
The exact way Abilify (or any other medicine for schizophrenia) works is unknown. However, experts believe that Abilify works by adjusting dopamine, instead of completely blocking it, as well as affecting serotonin.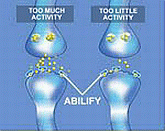
We now understand that schizophrenia is an illness, and, like any illness, it can be treated with medication.
David Daniel, MD, psychiatrist, George Washington University
You have reason to be hopeful
Although a cure has yet to be found, schizophrenia is a treatable illness.
Medicines are available that can help people better manage their symptoms.
Increases in blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), in some cases serious and associated with coma or death, have been reported in patients taking medicines like Abilify. Lightheadedness or faintness caused by a sudden change in heart rate and blood pressure when rising quickly from a sitting or lying position (orthostatic hypotension) has been reported with Abilify. Medicines like Abilify can affect your judgment, thinking, or motor skills. Other common side effects include: constipation, an inner sense of restlessness or need to move (akathisia), headache, nausea, upset stomach, vomiting, agitation, anxiety, insomnia, sleepiness, lightheadedness, and tremor.
 © 2006 Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
© 2006 Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
















 You may have heard that some treatments for mental illness cause diabetes. Take a closer look at the facts.
You may have heard that some treatments for mental illness cause diabetes. Take a closer look at the facts.